

Sep 28, 2022
The construction industry has made a significant shift in the last decade by adopting and leveraging small Unmanned Aircraft Systems (sUAS) technology, commonly referred to as drones. Historically, drone technology on active construction sites was used for safety purposes, but now construction managers are embracing the full potential of the drone’s power. According to Report Ocean, a database focusing on technology for agriculture, the global market value for construction drones in 2019 totaled $4.8 million. That number is projected to reach roughly $12 million by 2027. Drones are becoming a standard practice within the construction industry, most universally for the efficiency in aerial mapping of sites. The quality and quantity of data captured exceeds that of other technologies, arming owners and stakeholders with precise data and intel, with a time and cost savings, required to make strategic decisions about project sites.
Aerial Mapping Sets New Benchmarks in Site Visualization
Rapidly, drones have become one of, if not the primary, implementation method of photogrammetry, the science of gathering reliable data on physical objects and the environment. This technology, matched by improvements in software and photo resolution, has created site mapping like never before. Construction companies are eagerly transitioning to these improved processes to better understand their sites and surrounding areas.
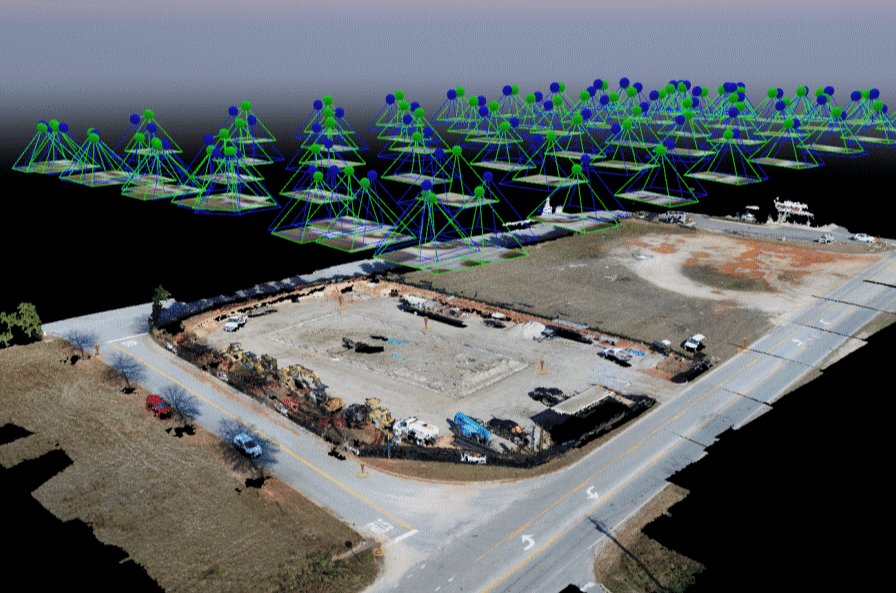

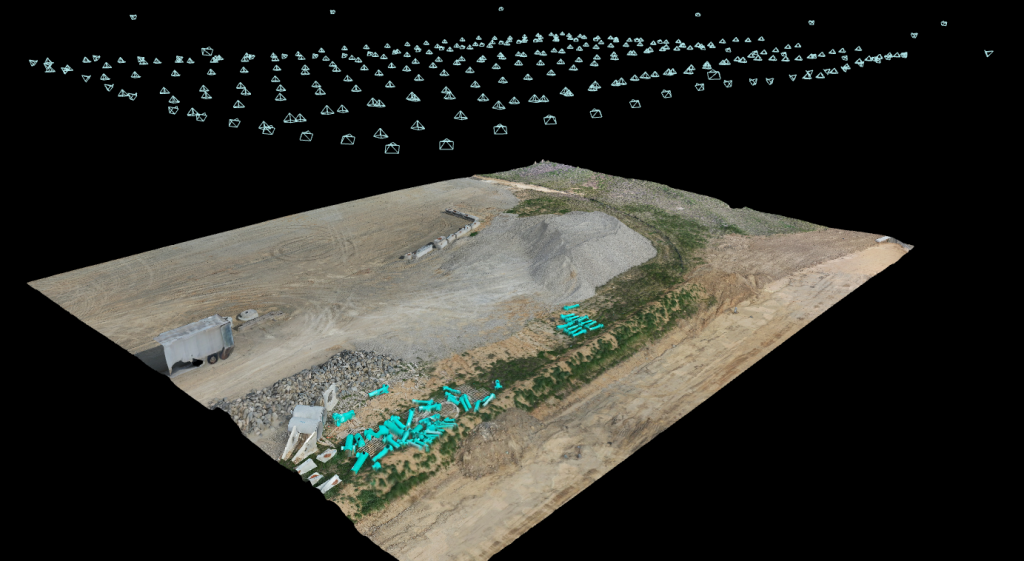
Photogrammetry uses drone images to reconstruct a job site in a 3D model with image overlap. Overlapping photos of a site gives the software a chance to triangulate and develop a point cloud based on each photo’s location, camera angle, and many other factors.
These point clouds are sets of data points in a given space that create realistic models that can be measured and manipulated. The technique has been refined and made readily available as use cases are intertwined with the drone industry’s growth. Drones have made site mapping faster, less invasive, and more accurate than previous aerial and terrestrial mapping methods.
Aerial Imaging Unlocks Construction Site Data
When deciding where and how to build, a thorough land survey that examines topography and soil types is an integral first step. These existing site conditions are two of the most important components when understanding a site’s potential. Differences in soil require detailed foundation considerations, whereas severe topography presents a whole new range of earthwork strategies. Accurately assessing these two factors saves time and money in design and execution.
Site surveying combines photogrammetry and laser imaging, detection, and ranging (LiDAR) to accurately reconstruct the world, virtually. Traditional survey equipment is expensive, requires specific training, an experienced team to implement, and can take hours and several site visits to complete. Construction drones, through photogrammetry, can capture 120 acres of land in roughly 30 minutes and produce detailed models reaching similar accuracy to traditional techniques, within 1-2%. This stark comparison to traditional techniques conveys drone technology as the path for future site surveying and upon completion, construction companies can begin making considerations on how to approach the site.
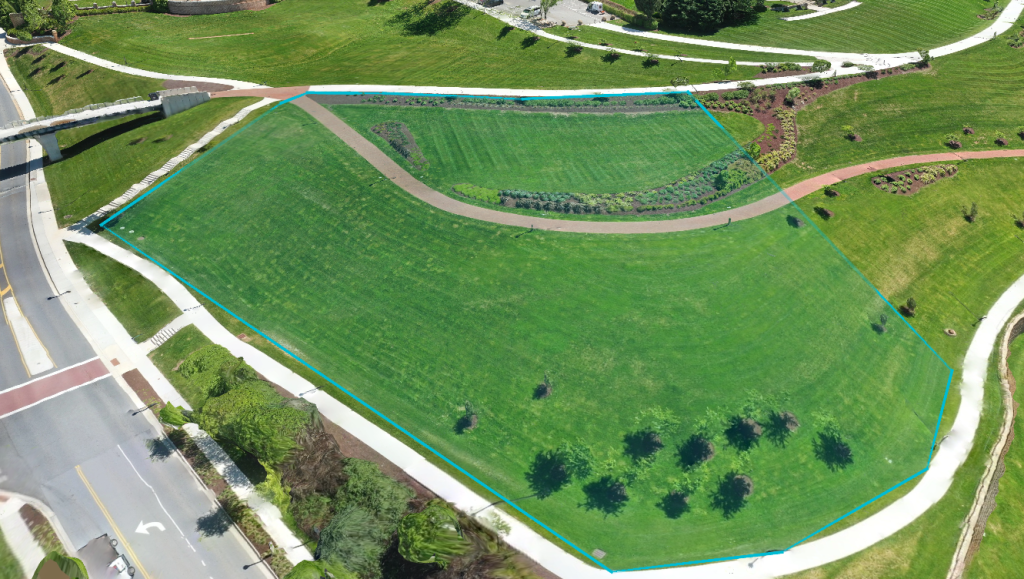

Using Aerial Volumetrics for Site Selection
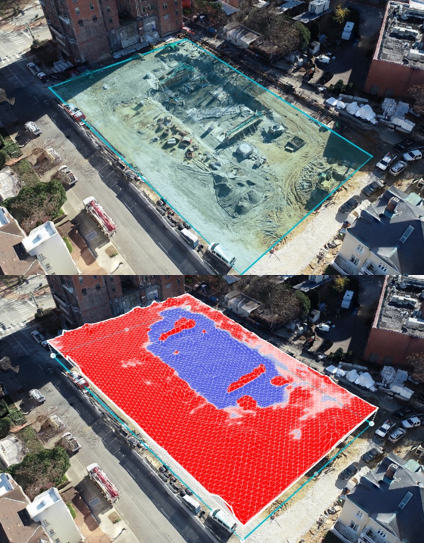
In preparing a site for construction, site logistics planning evaluates the amount of earth that needs to be moved, as earthwork can impact construction costs and schedule significantly. Drone mapping provides the construction industry with a unique and accelerated workflow to perform cut/fill analysis. Volumetrics can be extracted from the model to determine precise measurements of surface area, earth removal, and backfill. These measurements can be pulled with a few clicks of a button with confidence in accuracy. Site analysis performed earlier in the project opens the possibility for better site utilization, focused on controlling the impact of earthwork on project cost and duration.

Drone Technology Maximizes Job Site Efficiency
It’s easy to see why drones have entered and taken over the surveying and mapping market. They provide high-quality data in a short amount of time over large swaths of land as a cheaper solution than traditional surveying. Construction companies, driven by time and cost, are revising their processes, and adopting the new aerial world. Drones will have a lasting impact on the speed and accuracy of site planning, especially with the evolution of technology continuing to improve and offer new capabilities.